Langraph
文章目录
langgraph 的关键概念
states 状态
功能: 一个 dict, 用来存储状态信息,历史聊天记录(messages)
特点:
不可变性
- State 需要是不可变的,因此使用时,在 node 内部不要修改输入的 state, 或者使用 state.copy() 后的版本
例子:
| |
nodes 节点
功能:类似一个处理单元,接收上一个 state, 处理后返回下一个 state
例子:
| |
edges 边
类型:两种边
无条件边:
gaph.add_edge()- 直接连接两个 node
添加边:
graph.add_conditional_edges()- 根据不同的条件连接不同 node, 类似 switch/dict 映射
条件边的要素
输入 node
- 输入 node 返回的 state, 包含的信息,可以帮助选择先一个 node 是哪个
route 路由函数
- 分析上一个 node 的 state, 确定下一个Node 是那个
- 输入: 上一个 node state
- 输出: str, 下一个 node 的名称
例子:
1 2 3 4 5def router_fun(state: State) -> str: if state.need_search == True: return 'search_node' else: return 'answer_node'
后续 nodes 信息
- router 返回数据和 node_name 的 mappping dict
例子:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10graph.add_conditional_edges("though_node", router_fun, { "search_node": "search_node", "answer_node": "answer_node" }) # mappping_dict # { # "search_node": "search_node", # "answer_node": "answer_node" # }
START, END 开始和结束节点
状态持久化
人工干预
Agent 概念
参考:
什么是 agent
一个包含了 llm (思考)、tools (感知或外部能力) 和 prompt (提供指令) 的智能体。 它能够把你的需求分解成tool 调用来解决和实现。
思考 –> 知道调用 tool –> (observe) 观察调用结果 –> 思考 –> 调用 tool (…) || 或者 结束给出最终答案
- ReAct
多智能体 Multi-Agent
参考:
两种架构模式
supervisior 模式(监督者架构)
- 有一个居中调度者
特点:
- 监督者居中协调 + 任务分配
swarm 模式(群体架构)
工具调用 ToolNode
- 多个 tools 的容器 node, 负责调用 tool, 支持多个tool call, 并行调用
Agent 上下文和记忆(长期记忆 Vs. 短期记忆)
持久化 persistence
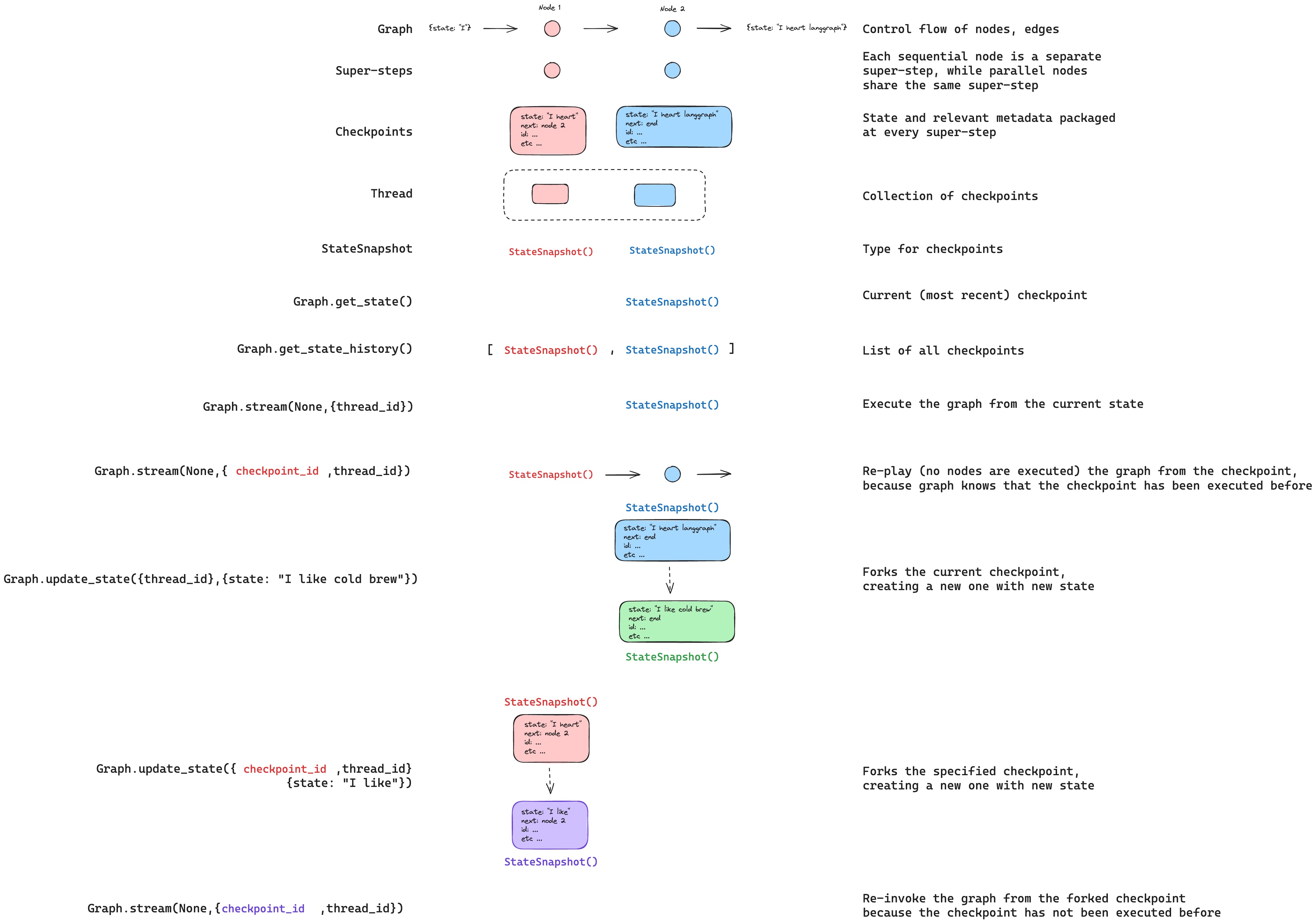
checkpoints
什么是 checkpoints:
- checkpoints 是用来保存 graph 的运行状态的持久化工具
作用:
- 单个 checkpoint 存储 super step 的 State 和 metadata 信息
使用逻辑
- checkpointer 可以通过 thread_id 隔离不同用户的历史记录
通过config 指定 thread_id, eg:
1 2config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "1"}} list(graph.get_state_history(config))- 通过 super steps 触发单个 checkpoint 的保存(snapshot)
重要概念
生成checkpoint 的点
- 单个 node
- 并行运行的 nodes
单个checkpoint (snapshot, StateSnapshot) 存储的信息:
- config
- metdata
- values: 给定 node 的 values(一个dict)
- next: 下一个要执行的 node
获取存储的历史数据
参考:
查询历史方法:
最新状态查询 / 给定用户(thread_id) 的状态查询
checkpointer.get_state(config)- 单个 StateSnapshot 对象
- type:
StateSnapshot
整个历史查询
checkpointer.get_state_history(config)- type:
list[StateSnapshot]
回放 replay
回放的过程:
- 输入: (thread_id, checkpoint_id)
- checkpoint_id 之前的 steps 不执行,知识演示
- checkpoint_id 之后的 steps 执行
| |
代码阅读
create_react_agent
判断是否继续(终止循环调用 tool 的方法)
判断最后一个 message 是否包含 tool call
| |
存储信息
- state.remaining_steps : 剩余步骤计数
tool.return_directly : 工具调用完成后,是否是直接返回,不需要额外推理
- 出现这种 tool 调用成功后,需要直接中断 graph 调用
- 比如:有的 tool 可以给出直接答案,这种就不需要额外的思考过程
FAQ
递归深度限制
默认递归深度为 25,可以通过 config={"recursion_limit": 100} 调整,防止无限循环。
| |
文章作者
上次更新 2025-09-24 (360d44c)